In manufacturing, metal stamping is a critical process for producing high-quality, precise components across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
As the demand for efficiency and cost-effectiveness grows, manufacturers need to understand the factors that impact metal stamping prices.

The price of metal stamping is determined by several key factors, including material selection, tooling investment, design complexity, production volume, and market conditions.
Each of these elements contributes to the overall cost structure, and understanding how they interact can help businesses optimize their production process, reduce waste, and manage expenses effectively.
Now, let’s delve deep into the most influential factors affecting metal stamping prices, providing practical insights and strategies to help businesses optimize their operations and manage costs effectively.

What Are the Key Factors Impacting Metal Stamping Prices?
1. Material Selection
Material selection is one of the most critical factors in determining metal stamping costs.
Different materials vary in price, availability, and suitability for specific applications. Some key considerations include:
1. Type of Metal:
o Aluminum: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and relatively affordable for high-volume applications.
o Stainless Steel: Durable and corrosion-resistant but more expensive than standard steel.
o Exotic Alloys: Materials like titanium or nickel are often required for specialized applications but come at a premium.
2. Market Conditions:
o Global events, tariffs, and supply chain disruptions can significantly affect material costs. For example, tariffs on imported steel or aluminum can lead to price surges.
o Geopolitical tensions may restrict access to certain materials, driving up prices.
3. Material Wastage: Efficient material usage minimizes scrap, directly impacting costs. Collaborating with experienced suppliers can help reduce waste and optimize material selection.
The choice of material significantly impacts your final product cost. For detailed guidance on material selection, check our comprehensive guide on choosing the right metal for sheet metal fabrication.
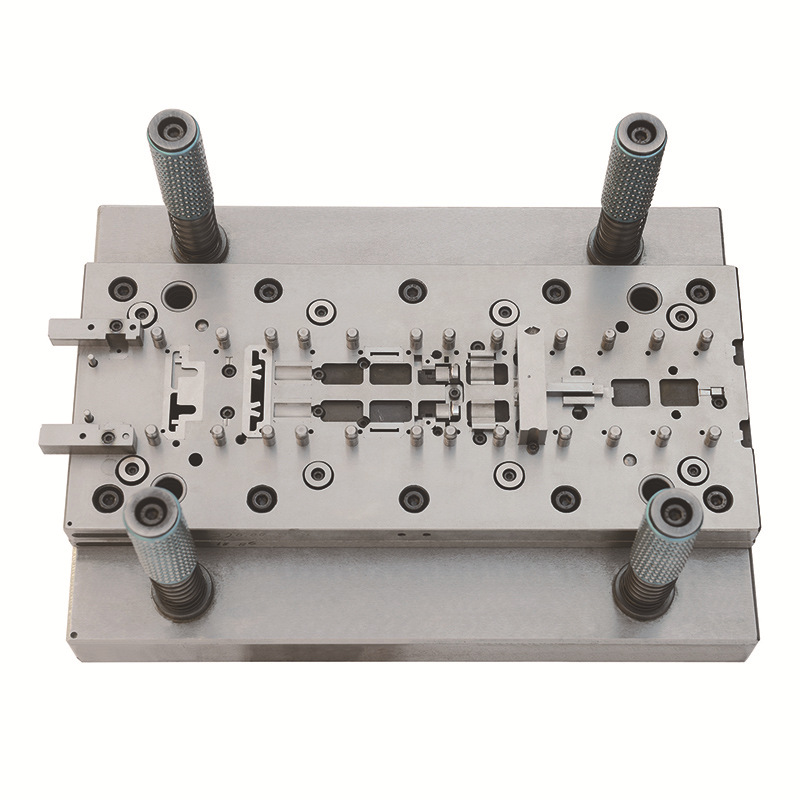
2. Tooling Investment
The investment in tooling for metal stamping is another significant cost driver.
Tooling includes custom dies and tools used in the stamping process, and the complexity of these tools can vary depending on the part design.
1. Die Complexity:
o Simple dies for standard shapes are relatively inexpensive.
o Complex dies with intricate features, such as multiple bends or embossing, require advanced engineering, driving up costs.
2. Tool Longevity:
o High-quality tooling materials like hardened steel are more expensive but last longer, reducing long-term costs.
o Frequent maintenance and replacements for lower-quality dies increase total costs over time.
Understanding die longevity is crucial for cost planning. Learn more about tool lifespan in our detailed metal stamping die durability guide.
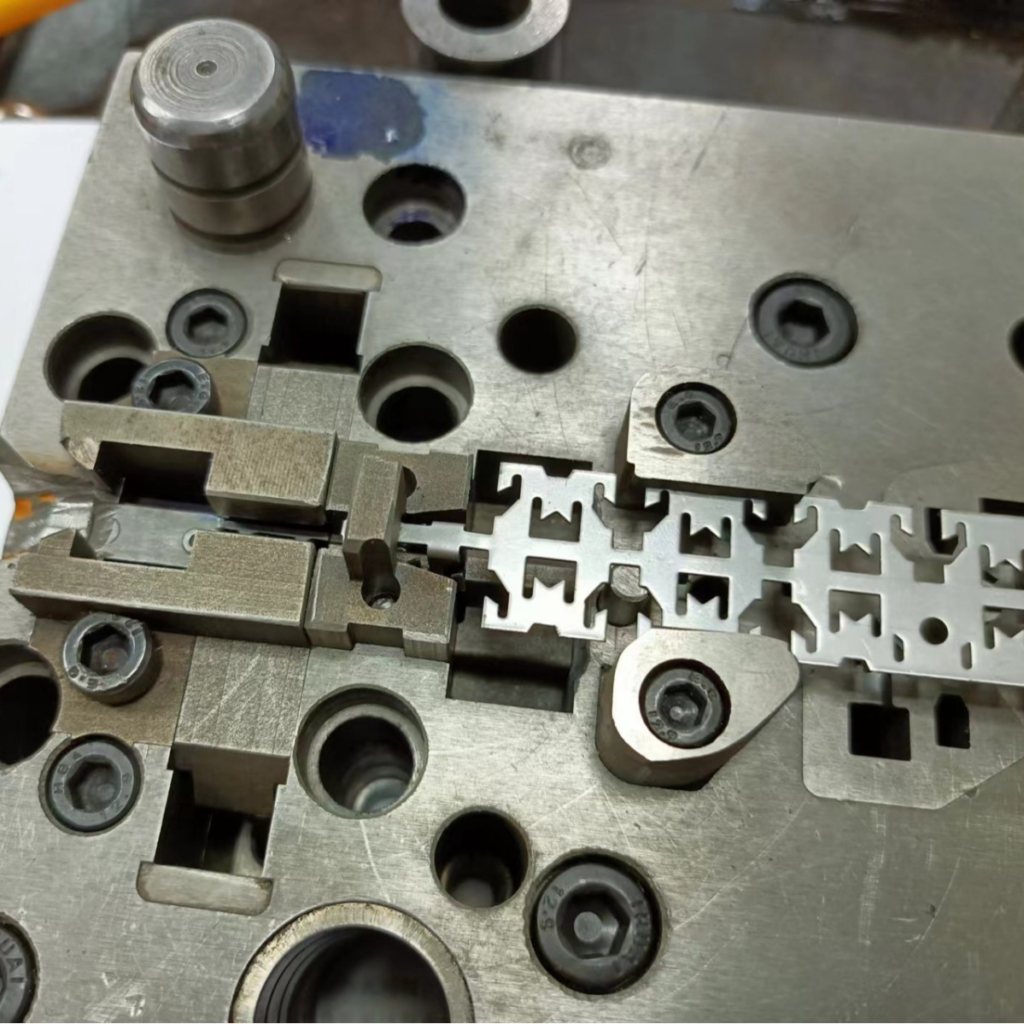
3. Design Complexity
Design complexity directly affects the number of production steps, tooling requirements, and the precision needed in manufacturing.
Parts with intricate designs and tight tolerances require more specialized tools and higher expertise.
1. Tighter Tolerances:
o Precision machining to achieve tight tolerances demands advanced tools and skilled operators, increasing costs.
o Relaxing tolerances where possible can significantly lower expenses.
2. Design Features:
o Adding features like perforations, embossing, or bends requires additional processing.
o Streamlining designs without compromising functionality can lead to significant cost reductions.
3. Prototyping:
o Complex designs often need multiple prototypes for testing and validation.
Investing in Computer-Aided Design (CAD) simulations can reduce the need for physical prototypes and lower costs.
4. Production Volume (EAU)
The estimated annual usage (EAU), or the number of units to be produced, is a critical factor in determining the cost of metal stamping.
Production volume influences economies of scale and can lead to substantial cost savings.
1. Economies of Scale:
o High production volumes allow manufacturers to spread out fixed costs, such as tooling and setup, across many units.
This lowers the per-unit price, making high-volume runs much more cost-effective.
2. Batch Production:
o Large batches also minimize setup times and machine downtime, leading to faster production cycles and lower costs.
3. Demand Forecasting:
o Accurately predicting demand ensures businesses can balance production volumes effectively.
Overestimating demand can lead to excess inventory, while underestimating demand may necessitate costly retooling or smaller follow-up batches.
5. Market Conditions
Global and local market conditions significantly influence metal stamping costs. Some key factors include:
1. Energy Costs:
o Metal stamping is energy-intensive, and fluctuations in electricity or fuel prices can directly affect operational costs.
2. Labor Costs:
o Regions with higher labor rates may experience increased production costs, but automation can help offset these expenses in the long run.
3. Supply Chain Disruptions:
o Events like port closures, raw material shortages, or pandemics can disrupt supply chains and inflate costs.
o Diversifying suppliers and maintaining inventory buffers can mitigate these risks.

What are the Key Limitations of Metal Stamping in Cost Management?
While metal stamping offers numerous advantages, it has limitations that must be considered:
1. Material Thickness:
o Stamping is best suited for thin to moderately thick materials. Excessively thick materials can lead to higher tooling wear or even equipment damage.
2. Design Constraints:
o Extremely complex shapes may require alternative methods or multi-step stamping processes, increasing costs.
3. Initial Investment:
o The upfront cost of tooling can be prohibitive for low-volume production.
Recognizing these limitations helps businesses decide when to use stamping versus other manufacturing methods.
How Can You Optimize Metal Stamping Costs?
Understanding the key cost factors is the first step to optimizing metal stamping prices.
Here are some actionable strategies to reduce costs:
1. Optimize Material Selection:
o Choose materials that balance performance with cost-effectiveness. Collaborate with suppliers for the best options.
2. Simplify Designs:
o Streamline part designs to eliminate unnecessary complexity while maintaining functionality.
3. Increase Production Volumes:
o Leverage economies of scale by consolidating orders or producing in larger batches.
4. Work with Reliable Suppliers:
o Experienced suppliers often offer insights into cost-saving measures and efficient processes.
5. Invest in Automation:
o Automating repetitive tasks can lower labor costs and increase production efficiency.
6. Regular Maintenance:
o Keeping tools and equipment in optimal condition reduces downtime and repair costs.

Conclusion
Metal stamping costs are influenced by various factors, including material selection, tooling investments, part design complexity, production volume, and market conditions.
By understanding these variables, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize operations and control expenses.
Whether you’re an engineer, manufacturer, or business owner, leveraging this understanding helps you navigate the complexities of pricing in the metal stamping industry and stay ahead of the competition.









