Heat management is a critical aspect in the design and operation of electronic devices, automotive systems, and industrial machinery.
Effective heat dissipation ensures optimal performance and longevity. Aluminum heat sinks have become the preferred solution due to their unique properties and advantages.
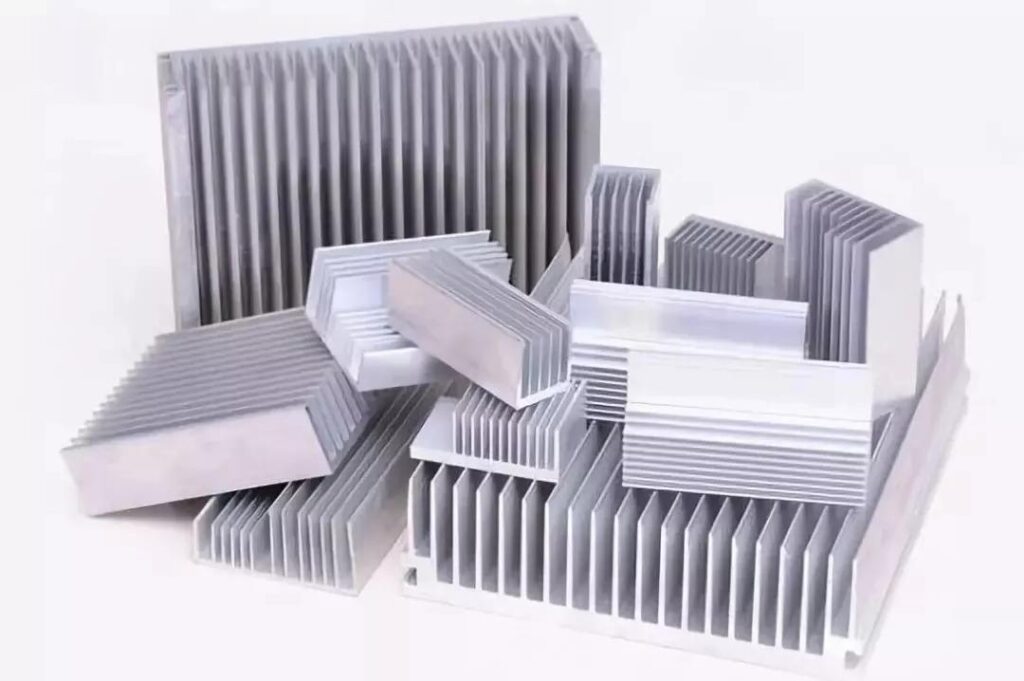

Aluminum heat sinks offer high thermal conductivity, lightweight design, cost-effectiveness, etc. These advantages make them ideal for various applications, including electronics, automotive systems, and industrial machinery. They efficiently dissipate heat, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of devices.
If you want to continue exploring what make aluminum a preferred choice in many industries, now let’s go deeper into the advantages of aluminum heat sinks.
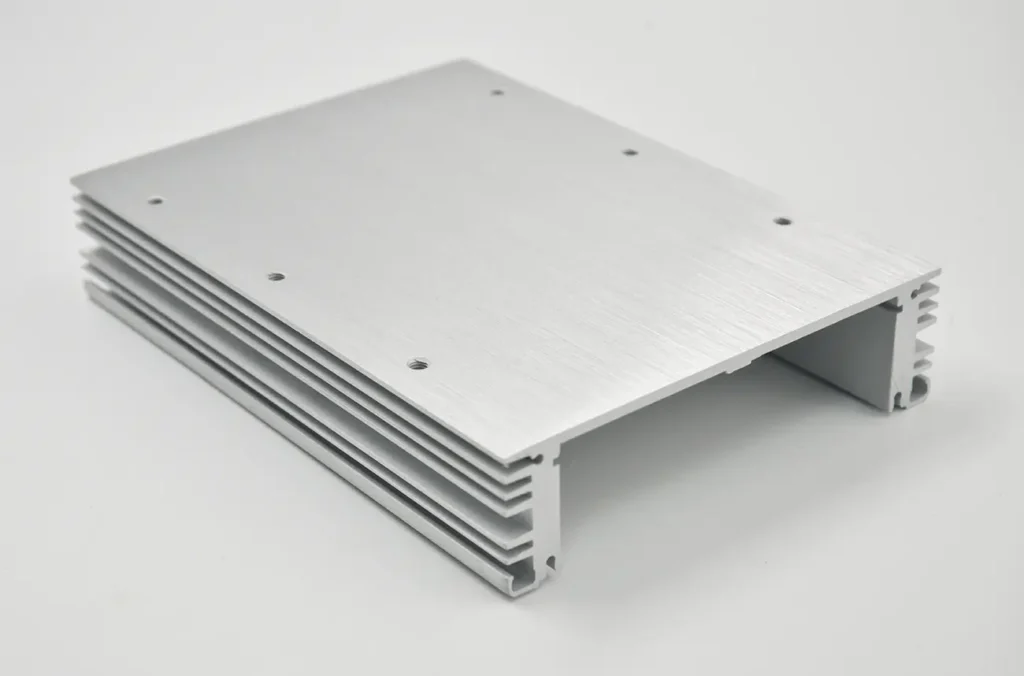

Why is Aluminum Used for Heat Sinks?
Aluminum is used for heat sinks because of its excellent thermal conductivity, which allows it to absorb and dissipate heat effectively. Additionally, aluminum is lightweight, which makes it suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in portable electronic devices and automotive systems.
The material is also relatively inexpensive compared to other metals like copper, making it a cost-effective solution for large-scale production. Moreover, aluminum has good corrosion resistance, which enhances the durability and lifespan of the heat sinks.
Aluminum’s ease of manufacturing also plays a crucial role in its widespread use for heat sinks. The material can be easily extruded, stamped, and machined into various shapes and sizes, allowing for customized designs
This flexibility in manufacturing enables engineers to create heat sinks that are optimized for maximum thermal performance while maintaining a lightweight and cost-effective structure.
Furthermore, aluminum’s recyclability adds to its appeal. The metal can be recycled multiple times without losing its properties, making it an environmentally friendly option.
This is particularly important in today’s world, where sustainable practices are increasingly prioritized. By choosing aluminum heat sinks, manufacturers can contribute to reducing the environmental impact of their products.
What Are the Advantages of Aluminum Heat Sinks?
The benefits of aluminum heat sinks include:
• High Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum’s thermal conductivity is sufficient for efficiently transferring heat away from components. This ensures that electronic devices and systems can operate at optimal temperatures, preventing overheating and potential damage. Effective thermal management is crucial in maintaining the reliability and performance of electronic components, especially in high-power applications.
• Lightweight: The low density of aluminum makes it ideal for applications where weight savings are important. For instance, in the automotive industry, reducing the weight of components can lead to improved fuel efficiency and better overall vehicle performance. Similarly, in aerospace applications, lightweight materials are essential for achieving the desired performance and fuel efficiency.
• Cost-Effective: Aluminum is more affordable than other metals with similar thermal properties. This cost advantage makes aluminum heat sinks an attractive option for manufacturers looking to balance performance and budget. The cost savings can be significant, especially in large-scale production, where the cumulative effect of using a less expensive material becomes more pronounced.
• Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer that prevents corrosion, extending the life of the heat sink. This property is particularly beneficial in harsh environments where components are exposed to moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive elements.
• Versatility: Aluminum can be easily extruded into various shapes and sizes, allowing for customized heat sink designs to fit specific applications. This versatility enables engineers to optimize the thermal performance of heat sinks by designing fins, channels, and other features that enhance heat dissipation. Customization is particularly important in applications where space constraints and thermal requirements vary widely.

Aluminum vs Copper Heat Sinks
When choosing between aluminum and copper heat sinks, several factors need to be considered:
• Thermal Conductivity: Copper has a higher thermal conductivity, which can be beneficial for very high-power applications. However, in many cases, the thermal performance of aluminum is sufficient to meet the cooling needs of the application.
• Weight: Aluminum is significantly lighter than copper, making it more suitable for weight-sensitive applications. This is particularly important in portable electronic devices, automotive, and aerospace applications where minimizing weight is a key design consideration.
• Cost: Aluminum is less expensive than copper, making it a more cost-effective solution for many applications. The cost savings associated with using aluminum can be significant, especially in large-scale production.
• Corrosion Resistance: Both materials have good corrosion resistance, but aluminum’s natural oxide layer offers excellent protection. This makes aluminum heat sinks more durable in harsh environments where exposure to moisture and chemicals is a concern.
• Manufacturability: Aluminum is easier to extrude and machine, allowing for more versatile heat sink designs. The flexibility in design and manufacturing processes enables engineers to create heat sinks that are optimized for specific applications, improving overall thermal performance.

Applications of Aluminum Heat Sinks
Aluminum heat sinks are used in a wide range of applications:
• Electronics: Cooling CPUs, GPUs, power supplies, and other electronic components. In consumer electronics, effective heat management is crucial for maintaining performance and reliability.
• Automotive: Managing heat in LED headlights, power electronics, and engine components. In the automotive industry, aluminum heat sinks help improve the performance and longevity of various systems.
• Industrial Machinery: Cooling motors, drives, and other industrial equipment. In industrial applications, aluminum heat sinks ensure that machinery operates within safe temperature limits, preventing overheating and potential failures.
• Renewable Energy: Managing heat in solar inverters, wind turbine converters, and battery packs. In renewable energy systems, efficient thermal management is essential for maintaining the performance and lifespan of critical components.
• Aerospace: Cooling avionics, power systems, and other components. In aerospace applications, lightweight and effective thermal management solutions are critical for achieving desired performance and efficiency.

Summary:
To sum up, aluminum heat sinks provide a versatile and efficient solution for thermal management in various applications, offering significant advantages in terms of performance, weight, and cost.
Whether for electronics, automotive, or industrial use, aluminum heat sinks ensure devices run smoothly and reliably by keeping them cool. The material’s high thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, cost-effectiveness, and corrosion resistance make it an ideal choice for a wide range of heat dissipation needs.









