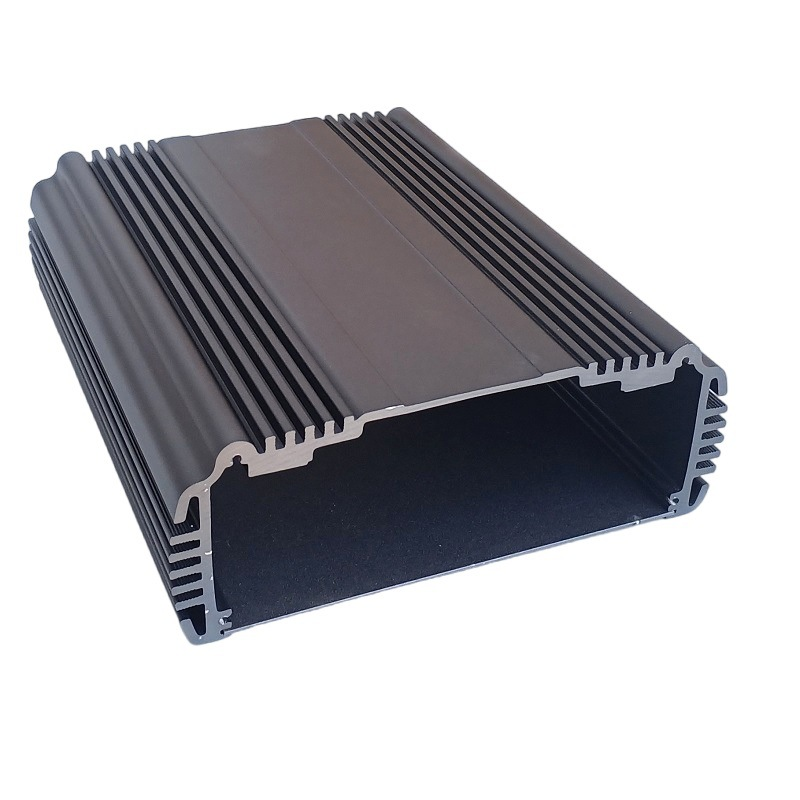
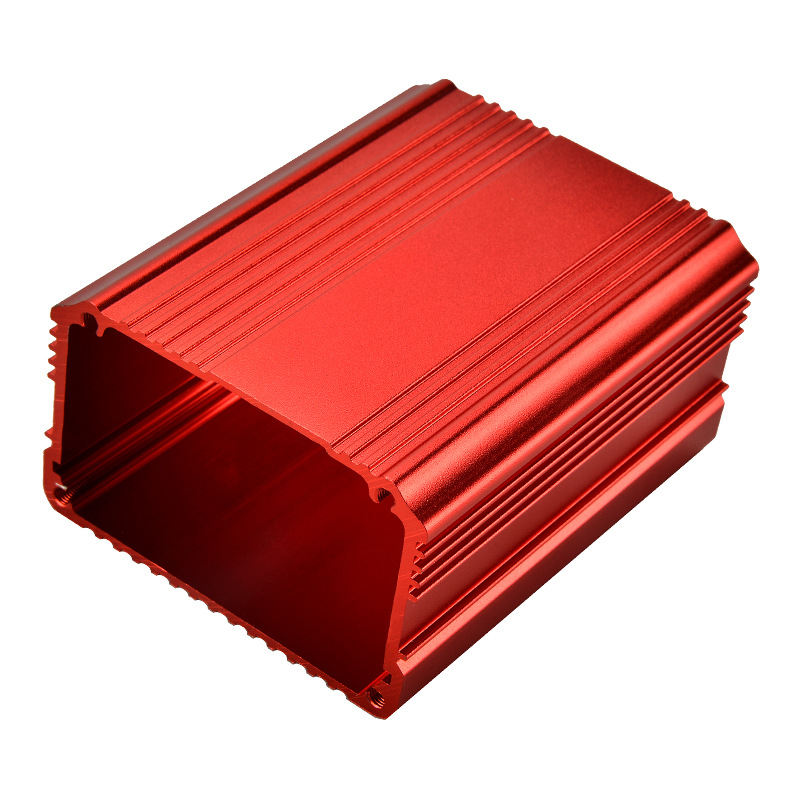
Aluminum extrusion is a versatile and widely-used process in various industries, transforming aluminum alloy into countless products.
This technique is essential for creating complex shapes with high precision and efficiency, making it a favorite for many engineering and manufacturing needs.

Aluminum extrusion is a manufacturing process where aluminum alloy is heated and then forced through a die with a specific cross-sectional profile.
This process allows for the creation of complex shapes that can be used in a variety of applications, from automotive parts to construction materials.
By understanding the aluminum extrusion process, its diverse applications, and the numerous benefits it offers, we can appreciate why this method is so valuable in today’s industrial landscape. Now, let’s explore the world of aluminum extrusion.
The Aluminum Extrusion Process
The aluminum extrusion process involves several critical steps to transform raw aluminum into finished products. Here is a detailed overview of the process:
Step 1: Preheating the Aluminum Billet
The process begins with an aluminum billet, a cylindrical log of aluminum. This billet is preheated to a specific temperature to make the aluminum malleable enough for extrusion but not molten.
Step 2: Extrusion
Once heated, the aluminum billet is placed into an extrusion press. A hydraulic ram then forces the aluminum through a die, which shapes the material into the desired cross-sectional profile. The die can create solid, hollow, or semi-hollow shapes, depending on the design requirements.
Step 3: Cooling
After extrusion, the aluminum profile is cooled, typically using air or water. This cooling process helps solidify the shape and prepare the material for further processing.

Step 4: Stretching
The cooled aluminum profile is then stretched to correct any twisting or warping that occurred during the extrusion process. This ensures the final product meets the required specifications and tolerances.
Step 5: Cutting to Length
The extruded aluminum profiles are cut to the desired lengths, ready for further treatment or use in various applications.
Step 6: Aging
To enhance the mechanical properties of the aluminum, the extruded profiles often undergo a process called aging. This involves heating the profiles to a specific temperature and holding them there for a certain period, which strengthens the material.

Applications of Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum extrusions are used across various industries due to their versatility and strength-to-weight ratio. Here are some common applications:
Electronics
In the electronics industry, aluminum extrusions are commonly used for heat sinks, enclosures, and components.
Aluminum’s excellent thermal conductivity makes it ideal for dissipating heat generated by electronic devices, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
Automotive
The automotive industry extensively uses aluminum extrusions for structural components, such as frame rails and side rails.
The lightweight nature of aluminum helps reduce the overall weight of vehicles, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Construction
In construction, aluminum extrusions are used for window frames, door frames, support structures, and more.
The corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum make it ideal for outdoor applications, ensuring longevity and low maintenance.

Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector utilizes aluminum extrusions for solar panel frames, wind turbine components, and other renewable energy infrastructure.
Aluminum’s strength, corrosion resistance, and recyclability make it an excellent choice for sustainable energy solutions.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies on aluminum extrusions for various structural and non-structural components. The lightweight and high-strength properties of aluminum are essential for aircraft, where weight reduction is critical for fuel efficiency and performance.
Marine
In the marine industry, aluminum extrusions are used for boat hulls, decks, and other structural components. The corrosion resistance of aluminum makes it suitable for harsh marine environments, ensuring long-lasting performance and reducing maintenance costs.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum Extrusion
Advantages of Aluminum Extrusion
1. Lightweight and Strong
Aluminum is about one-third the weight of iron, steel, copper, or brass, making it ideal for applications where reducing weight is crucial without compromising strength.
This characteristic is particularly beneficial in industries where weight reduction can lead to significant performance improvements and fuel savings.
2. Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum naturally forms an oxide layer that protects it from corrosion, which is especially valuable in marine and construction applications, where exposure to harsh weather conditions and saltwater can lead to corrosion in other materials.
3. Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum is an excellent thermal conductor, making it perfect for heat sinks and other applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. It’s also a good electrical conductor, suitable for electrical applications.
4. Sustainability
Aluminum is highly recyclable, and the extrusion process itself has a lower environmental impact compared to other manufacturing methods.
Recycling aluminum requires only a fraction of the energy needed to produce new aluminum, making it an eco-friendly choice.
5. High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Aluminum extrusions offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, which is crucial for applications where both strength and lightweight are necessary.
This characteristic is particularly beneficial in the transportation industry, where reducing the weight of vehicles can lead to improved fuel efficiency and performance without compromising safety.
6. Resilience and Ductility
Aluminum extrusions are resilient and ductile, allowing them to withstand impacts and stresses without breaking.
This property is essential in applications where materials are subjected to dynamic loads and potential impacts, such as in automotive crash structures and construction materials.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Extrusion
1. Size Variances:
There can be inconsistencies in the size of extruded products due to the nature of the process. This may require additional quality control measures to ensure consistency.
2. Product Limitations:
While aluminum extrusion is versatile, there are limitations to the shapes and sizes that can be produced. Extremely complex or large profiles may be challenging to manufacture using this process.
3. Initial Setup Cost:
The initial cost of creating extrusion dies and setting up the process can be high, particularly for custom profiles. However, this cost is often offset by the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of large-scale production.

Summary:
Aluminum extrusion offers numerous advantages, from flexibility in design to cost-effectiveness and sustainability. Its applications across different industries highlight its importance and versatility.
Whether you’re in electronics, automotive, construction, or renewable energy, understanding the benefits of aluminum extrusion can help you make informed decisions for your projects.









