Copper skived heat sinks are revolutionizing the cooling industry with superior thermal performance.
Copper skived heat sinks deliver maximum heat dissipation in applications with limited space and high ventilation levels.
They are a cost-effective solution considering the low tooling cost and optimized fin surface area.
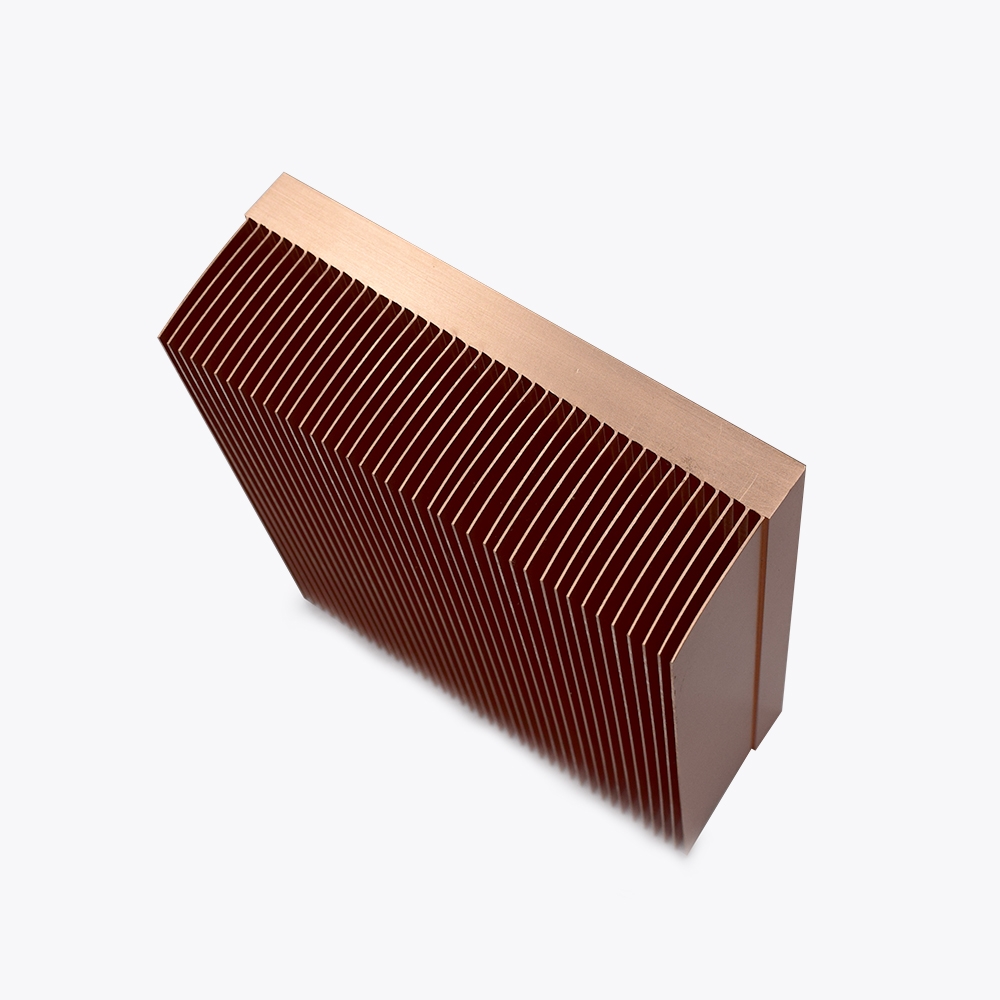
Suppose you are an engineer, production manager, or buyer looking for efficient heat dissipation solutions.
In that case, comprehensively understanding copper skived heat sinks can significantly impact your decision-making process.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the specifics of copper skived heat sinks and their numerous advantages.
-
Table Of Contents
-
1. The Advantages of Copper Skived Heat Sinks
-
2. Why Choose Copper Skived Heat Sinks?
-
3. How Do Copper Skived Heat Sinks Work?
-
4. When Should You Use Copper Skived Heat Sinks?
-
5. What is the Difference Between Skived and Extruded Heat Sinks?
-
6. Trade-offs of Choosing Materials for Heat Sinks
-
7. Summary
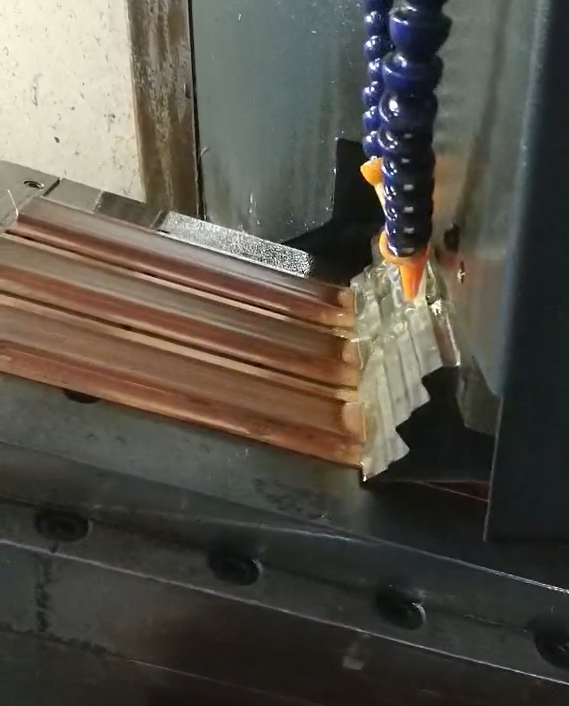

Why Choose Copper Skived Heat Sinks?
Copper, renowned for its exceptional thermal conductivity, is a preferred choice for heat sinks due to its capability to conduct and distribute heat rapidly.
Additionally, copper is highly resistant to corrosion, making these heat sinks more durable and long-lasting than those made from other materials.
The enhanced thermal performance of copper-skived heat sinks can lead to increased lifespan and reliability of electronic components.
One of the critical advantages of copper-skived heat sinks is their ability to maintain lower temperatures even under high thermal loads.
This is crucial for the longevity and reliability of electronic components.
Overheating can lead to thermal fatigue and eventual failure of components, which is costly and time-consuming to repair or replace. By effectively managing heat, copper-skived heat sinks help to prevent such issues and ensure continuous, reliable operation.
Another significant benefit is the cost-effectiveness of copper-skived heat sinks.
While the initial cost of copper may be higher than other materials like aluminium, the long-term benefits often justify the investment.
The superior thermal performance and durability of copper-skived heat sinks can lead to lower maintenance costs and reduced downtime, resulting in overall cost savings.
Copper-skived heat sinks are versatile and can be customized to meet specific design requirements.
The skiving process allows for the creation of complex fin geometries and varying fin densities, making it possible to tailor the heat sink to the specific needs of an application.
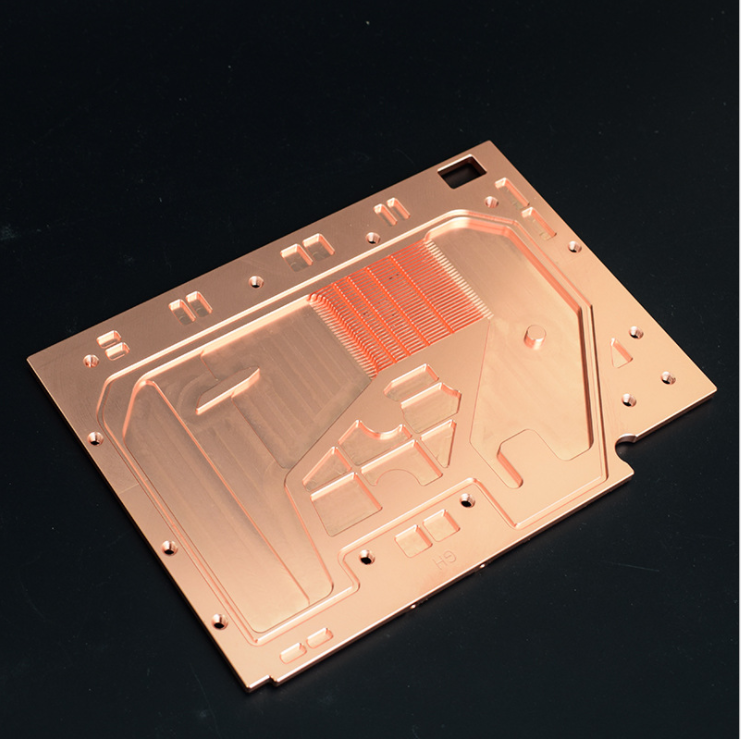
How Do Copper Skived Heat Sinks Work?
The working principle of a copper-skived heat sink involves absorbing heat from the heat-generating component and dissipating it into the surrounding air.
The heat sink’s base is in direct contact with the element, transferring heat from the component to the heat sink. The heat is then conducted through the copper fins, which increase the surface area for heat dissipation.
Airflow plays a crucial role in the cooling process. The increased fin density and thin fin design of skived heat sinks enhance airflow around the fins, allowing heat to be carried away more effectively.
This is particularly beneficial in applications with natural convection or forced air cooling. Heat transfer efficiency is significantly improved, ensuring that components remain within their optimal temperature range.
Additionally, the manufacturing precision of the skiving process ensures that each fin is uniformly cut and positioned, maximizing the contact area for heat transfer.
This uniformity is crucial for maintaining consistent thermal performance across the heat sink. The copper material further aids in this process by quickly spreading the heat along the fins, reducing hotspots and improving overall cooling efficiency.
When Should You Use Copper Skived Heat Sinks?
Copper-skived heat sinks should be used where maximum heat dissipation is required in confined spaces. They are particularly effective in environments with high levels of ventilation.
For instance, space is at a premium in compact electronic devices such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones. The ability to pack high-performance components into a small form factor necessitates efficient thermal management.
Copper-skived heat sinks are ideal for these applications due to their high fin density and superior thermal conductivity, ensuring heat is effectively dissipated even in tight spaces.
In densely packed circuit boards, such as those found in servers and data centres, efficient cooling is critical to prevent overheating and maintain reliable operation.
Copper-skived heat sinks provide thermal management to keep these systems running smoothly. The high fin density and optimized surface area of skived heat sinks allow for adequate cooling in environments where space is limited and thermal loads are high.
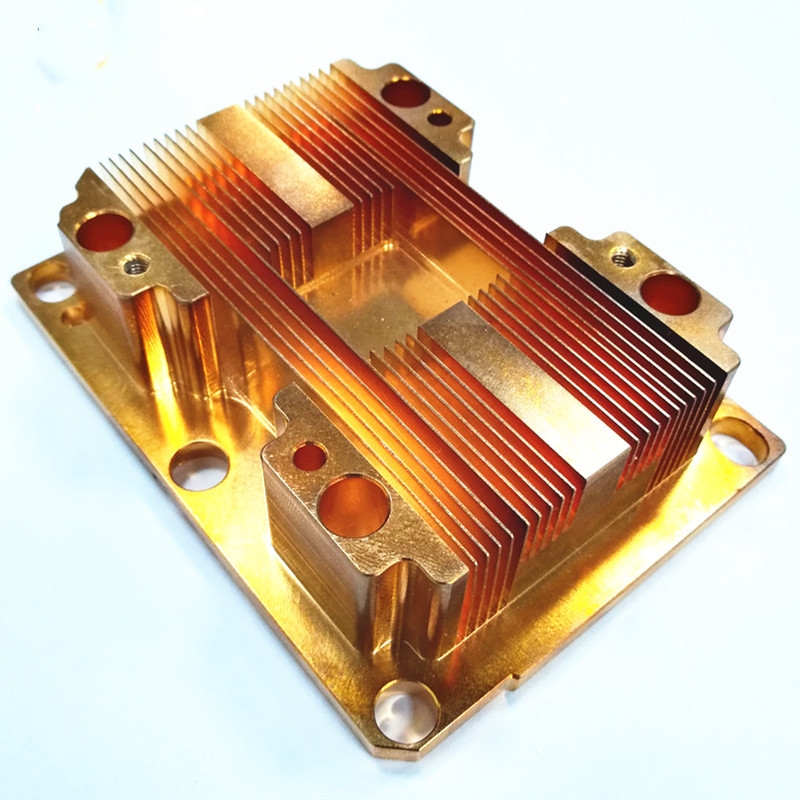
What is the Difference Between Skived and Extruded Heat Sinks?
The skiving process allows for greater fin density and thinner fins than extruded heat sinks. This results in better thermal performance and more efficient heat transfer.
Extruded heat sinks, typically made from aluminium, are formed by pushing material through a die, resulting in a less dense fin arrangement and lower thermal efficiency than skived heat sinks.
Skived heat sinks are made by cutting fins from a solid block of material, typically copper or aluminium. This process allows for the creation of ultra-thin fins that are closely spaced, maximizing the surface area for heat dissipation.
The high fin density and thin fin design of skived heat sinks provide superior thermal performance compared to extruded heat sinks.
In conclusion, while extruded heat sinks are more commonly used due to their lower cost and manufacturing flexibility, skived heat sinks offer superior thermal performance due to their high fin density and thin fin design.
Trade-offs of Choosing Materials for Heat Sinks
Copper is heavier than aluminium, which can disadvantage weight-sensitive applications.
Additionally, copper is more expensive than aluminium, which can impact the overall cost of the heat sink. Despite these drawbacks, the superior thermal performance of copper often justifies its use in high-performance and high-reliability applications.
While aluminium heat sinks are more commonly used due to their lower cost and lighter weight, copper heat sinks offer superior thermal performance.
Copper heat sinks are the better choice for applications where thermal management is critical, and the budget allows.
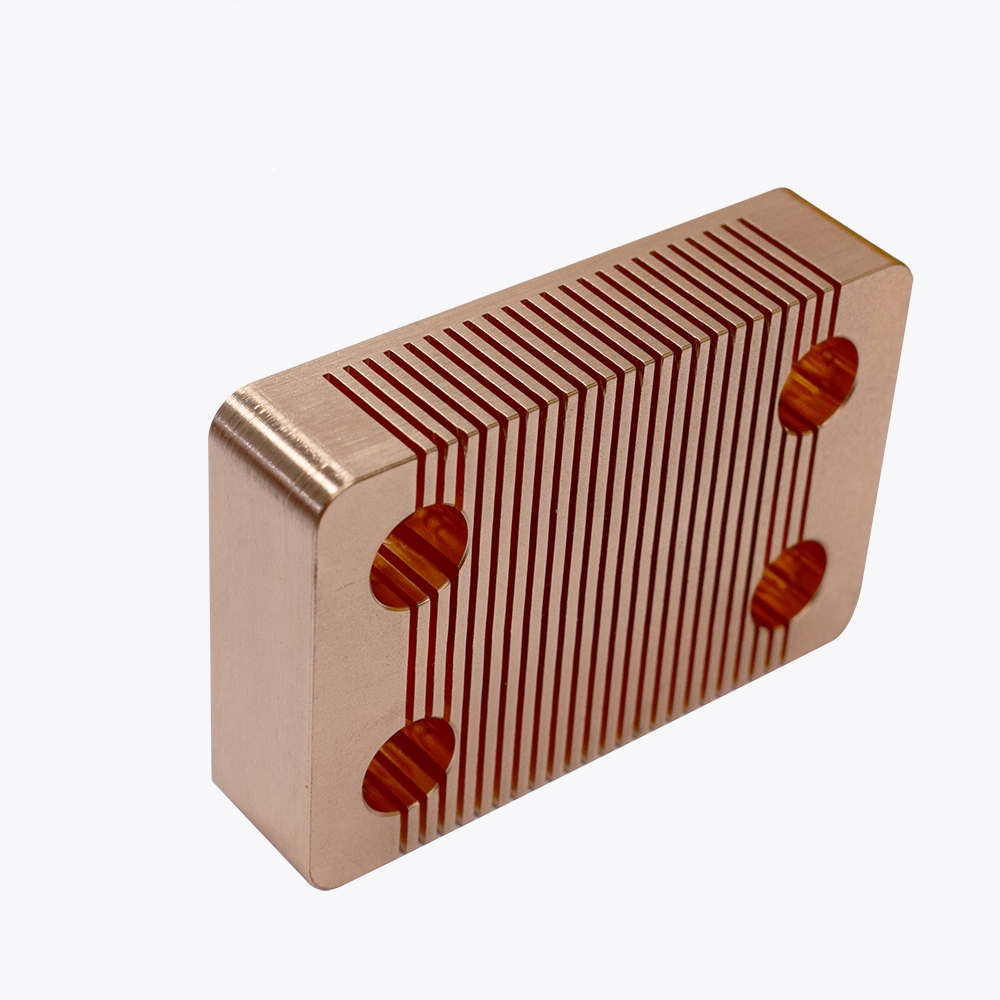

Summary:
Copper skived heat sinks offer unmatched thermal performance, making them a preferred choice for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation.
Their durability, cost-effectiveness, and superior thermal conductivity make them an excellent investment for engineers, production managers, and senior buyers.
Understanding when and why to use these heat sinks can significantly enhance your thermal management solutions.









