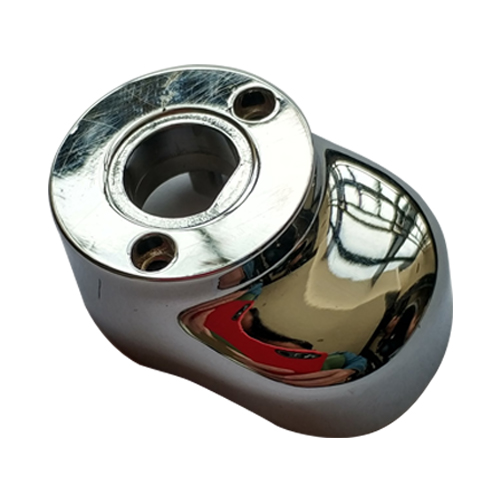
Die Casting Services
China Precision Aluminum Die Casting Manufacturer
Get the high-quality parts you need quickly with our all-in-one aluminum die casting expertise.
Typical Lead Time
Tooling = 4 weeks Samples = 1-2 weeks Production (Qty 10k) = Around 3-4 weeks
Cost Effective
Die casting can save money by reducing waste material and scrap.
100% Guarantee
ISO 9001 & ISO 13485 & IATF 16949 certified
Free Estimation
Select from a wide range of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.
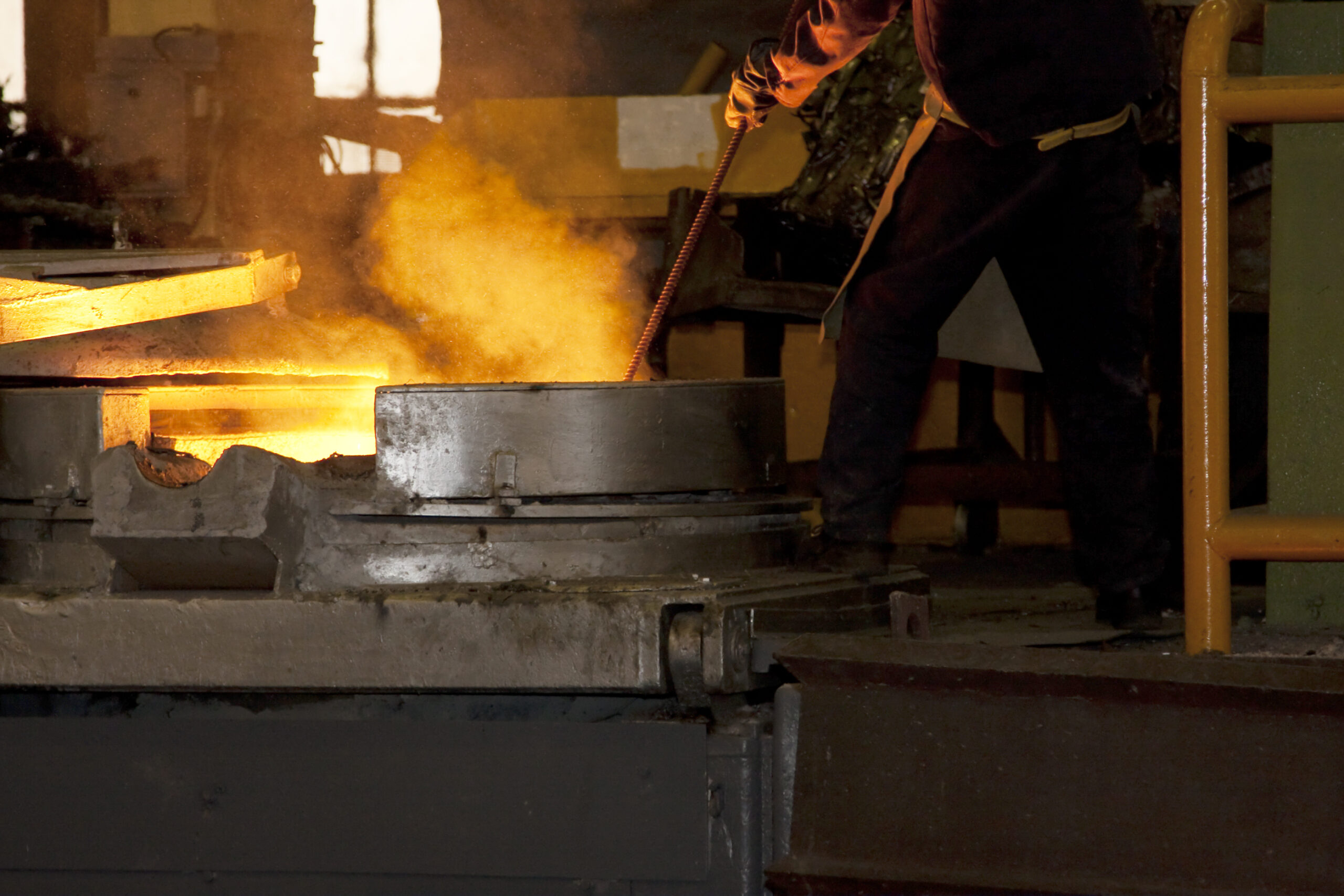

One Stop Die Casting Service
We offer many services beyond die casting. Our one-stop service includes everything from rapid prototyping to high-quality surface finishing. We make it easy for you to get the final product all in one place.
Our project managers and experts personally review and manually quote each die casting project to meet your unique needs, ensuring a fast and easy manufacturing experience. Learn more about our process and capabilities in the sections below.
Start Your Die Casting Parts

Start A Quote
Sample Approval

Production Begins

Capabilities

Engineering
Industries Served
Die Cast Metal Materials
Metals used in die casting are typically non-ferrous, such as bronze, aluminum, zinc, magnesium, or copper. Alloys, especially steel alloys, can also be used, but steel parts are usually forged instead.
GET YOUR CUSTOM DIE CAST COMPONENTS
When manufacturing with die casting, you can choose from several different metal materials. The material you select will depend on how you plan to use the product.
Available Finishes
Zinc and aluminum-zinc parts can be left as-cast and still resist corrosion. Aluminum parts need to be coated for corrosion resistance. Cast parts are usually separated from the casting sprue, leaving rough marks at the gate locations. Most castings will also have visible marks from the ejector pins. The surface finish for as-cast zinc alloys is usually 16-64 microinch Ra.
You can use sandblasting to peel paint, smooth out rust, take bumps and mars from stuff, and basically make things clean. Ironically, you can also sandblast things to scuff them up by etching the surface and give something a little bit of ‘tooth’ so that paint will stick better.
Type II anodizing enhances corrosion resistance. It allows parts to be colored in various shades like clear, black, red, and gold, typically for aluminum. Type III provides a thicker, wear-resistant layer as well as the corrosion resistance of Type II.
All die-cast parts can be powder coated. In this process, powdered paint is sprayed onto a part using static electricity, then baked in an oven. Powder coating creates a strong, wear- and corrosion-resistant layer that is more durable than regular painting methods. Many colors are available to achieve the desired look.
Die cast parts can be plated with electroless nickel, nickel, brass, tin, chrome, chromate, Teflon, silver and gold.
All die cast parts can be wet painted in a wide variety of paint formulations and colors.
Suppliers can add a chromate conversion coat to protect aluminum from corrosion and help paints and primers stick better. Chemical film conversion coatings are also electrically conductive.
Can't find the finish you require? Send us an RFQ, and we'll explore a finishing solution for you.
Design Guidelines
Before die casting your part, manufacturers will consider several factors, such as element thickness and details (which affect the time the metal spends in the mold) and the complexity of the design (which affects solidification time).
Tolerence
As cast tolerance as tight as +/- .005”, post machining available for tighter tolerance applications.
1
Finish
Typical surface finish of Ra 63 micro-inch as cast, post machining available for higher quality finishes.
2
Wall Thickness
Aluminum minimum wall thickness = .08”
3
Tolerence
Standard tolerance of +/- .005” for the first inch and +/-.002” each additional inch.
4
Draft
Minimum draft = .5 degrees
5
Wall Thickness
Zinc minimum wall thickness = .04”
6
You’ve got enough worries, let us take care of your parts.
QC will verify that the part material, features, and finish are in accordance with the part requirements specified in the PDF file, CAD file, and/or STEP file.
QC will conduct an examination using precise instruments to document every dimension, attribute, positional measurement, and specification as outlined in our Statistical Sampling Strategy.
QC will conduct a thorough inspection using a Coordinate Measurement Machine (CMM). This will document all dimensions, attributes, locations, and notes in accordance with our Statistical Sampling Plan.
The First Article Inspection aims to confirm that all engineering designs and specifications are fully understood, addressed, verified, and recorded. QC will keep a detailed quality log for customer oversight of responsibilities and planning. This includes conducting regular checks and audits to ensure compliance, assessing the root causes and corrective measures for any discrepancies, and investigating issues.
If your part needs additional inspections, such as Non-Destructive Testing, Serialization, Custom Sampling Plan, or if you want to use your own inspection datasheet, please let us know.
Die Casting Types
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Also known as gooseneck casting, the hot chamber die casting process is the most popular die casting method. It works best with low melting point alloys like zinc, magnesium, and lead.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
In the cold chamber die casting process, the chamber stays at room temperature. The metal is melted in a separate furnace, this method is suitable for materials with higher melting temperatures, like aluminum.
Vacuum Pressure Casting
In vacuum pressure die casting, the metal is placed in a chamber above the mold. Vacuum pressure pushes the metal into the mold cavity, where it cools and hardens. This method reduces turbulence from the metal’s movement and limits gas inclusions.
Low-Pressure Casting
In low pressure casting, molten metal is held in a chamber below the mold and pressurized to rise through a tube into the mold cavity. This method is used for making precise, symmetrical designs. Low pressure casting is most commonly used for aluminum components
Semi-Solid Die Casting
In semi-solid die casting, slugs are melted until slushy, then forced into a mold to cool and harden. Also known as thixoforming, offers a high degree of precision. This precise process is often used with aluminum, aluminum alloys, or magnesium alloys.
Squeeze Die Casting
Squeeze die casting starts with molten metal poured into an open die. The die then closes, forcing the metal into every corner. This process creates very dense parts. It is commonly used for metals with low fluidity and aluminum/aluminum alloys with high viscosity.
Die Casting Advantages and Disadvantages

we can help
Provide Customized Solutions
Contact Partzcore to get a free quote and expert advice on custom metal parts. Our team will provide the right solution for your project.
Tell Us What You Need
Please share your specific needs with us, including drawings, reference images, and your ideas, so we can turn them into reality.
Professional Team
We will analyze your requirements and drawings to provide the optimal solution, along with a detailed quote within 24 hours.
Approve for Mass Production
Upon receiving your approval and deposit, we will proceed with mass production and manage the shipping process.

