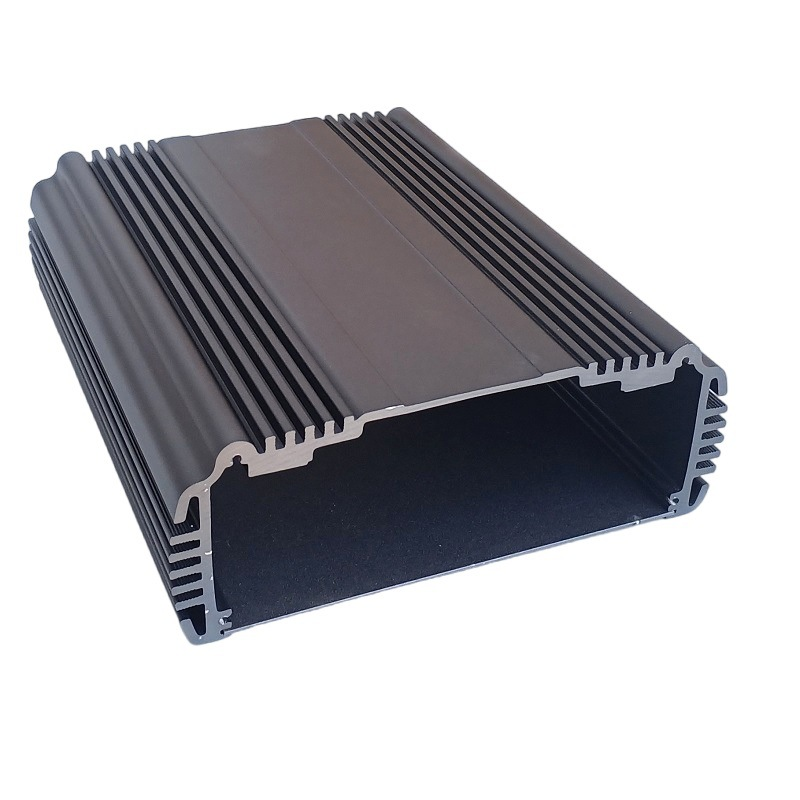
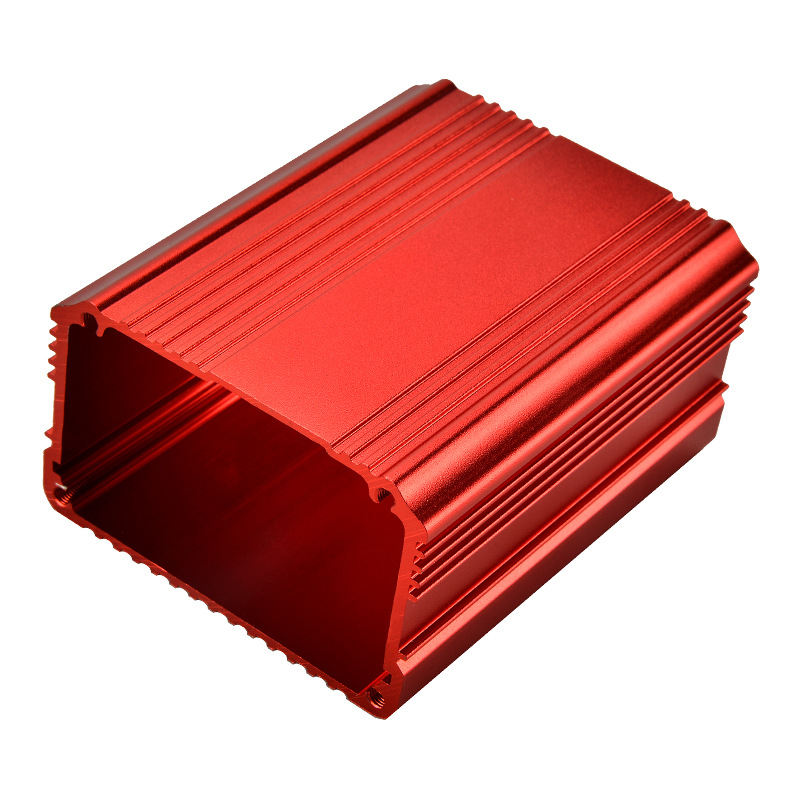
Managing heat efficiently is crucial for optimal performance and longevity in most of manufacturing tool.
This is where aluminum heat sinks come into play. But what exactly is aluminum heat sink design, and why is it so important?
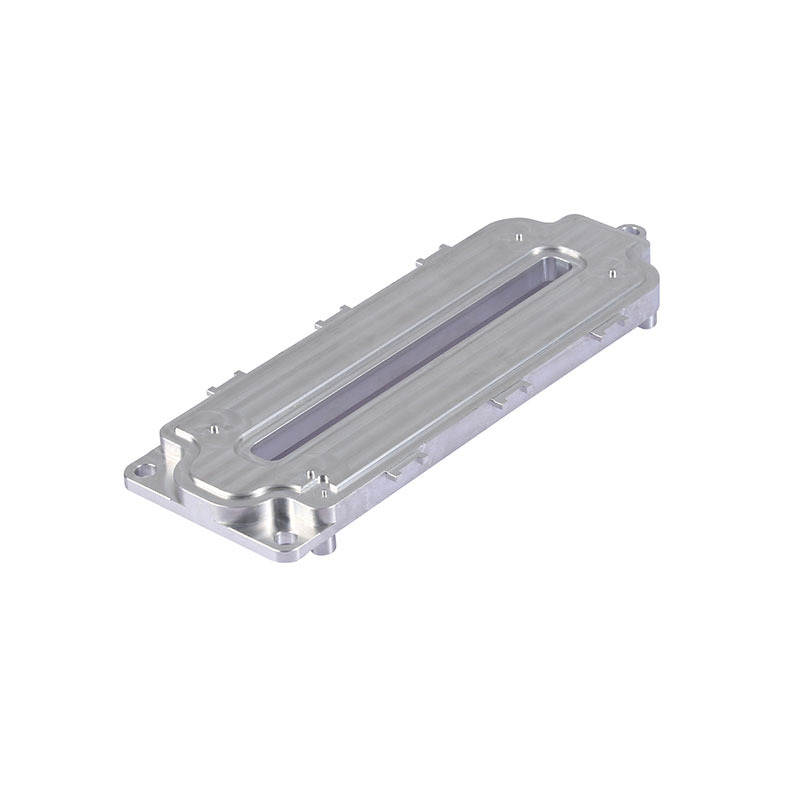

An aluminum heat sink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or liquid coolant, to prevent the device from overheating.
Aluminum is commonly used due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding the role and design of aluminum heat sinks is key to enhancing the efficiency of various electronic and mechanical systems.
Now, let’s dive into various aspects of aluminum heat sinks to understand their significance and functionality.
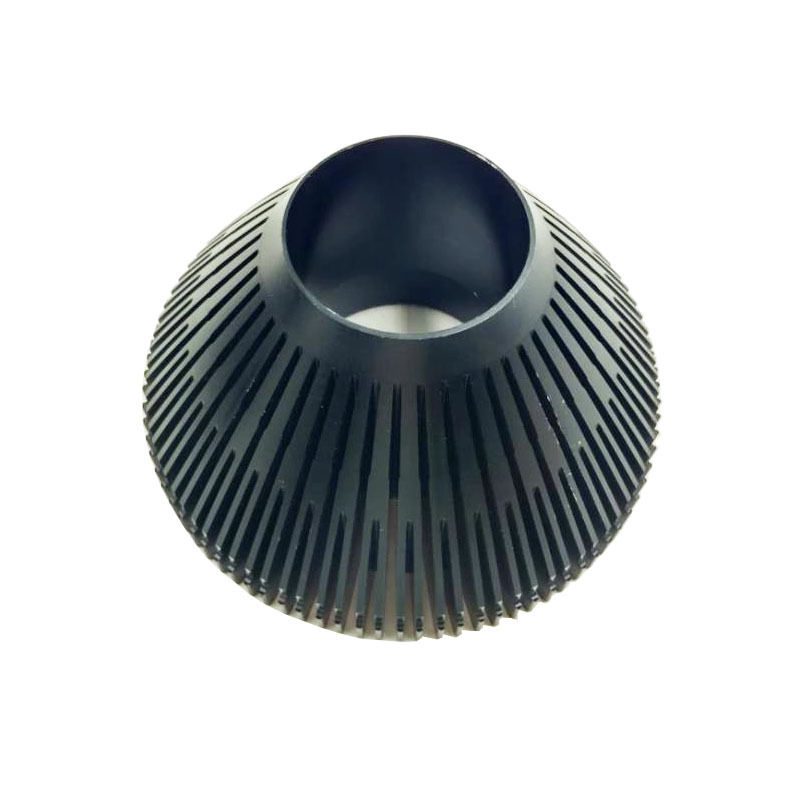

Why Is a Heat Sink Important?
Heat sinks are vital for maintaining the thermal stability of electronic devices. Without adequate cooling, components can overheat, leading to reduced performance, reliability issues, and potentially permanent damage.
Effective heat dissipation ensures that devices operate within safe temperature ranges, thereby extending their lifespan and improving efficiency.
Overheating can cause several issues, such as thermal throttling, where the device reduces its performance to cool down.
In extreme cases, overheating can cause permanent damage to the electronic components, leading to costly repairs or replacements. Therefore, selecting and designing an appropriate heat sink is critical for the reliable operation of electronic devices.
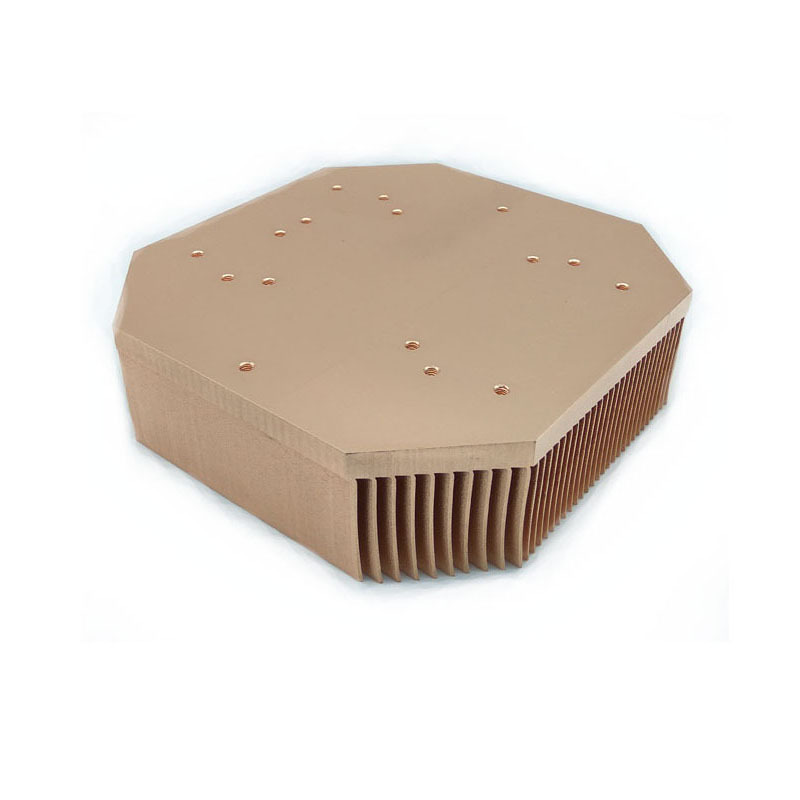

Different Types of Heat Sinks
Heat sinks come in various types, including active and passive. Active heat sinks use fans or other mechanical means to enhance cooling, while passive heat sinks rely on natural convection. Other types include:
• Bonded Fin Heat Sinks: Made by bonding individual fins to the base, allowing for customized fin arrangements. This type offers a good balance between performance and cost, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
• Stamped Heat Sinks: Produced by stamping fins from a single sheet of metal, making them cost-effective but less efficient. They are typically used in applications where cost is a primary concern and thermal performance requirements are moderate.
• Folded Fin Heat Sinks: Created by folding metal sheets into fins, offering a good balance of performance and cost. These heat sinks are often used in high-density electronic assemblies where space is limited, and efficient heat dissipation is critical.
Other specialized types include skived, extruded, and forged heat sinks. Each type has unique manufacturing processes and thermal characteristics, making them suitable for specific applications.
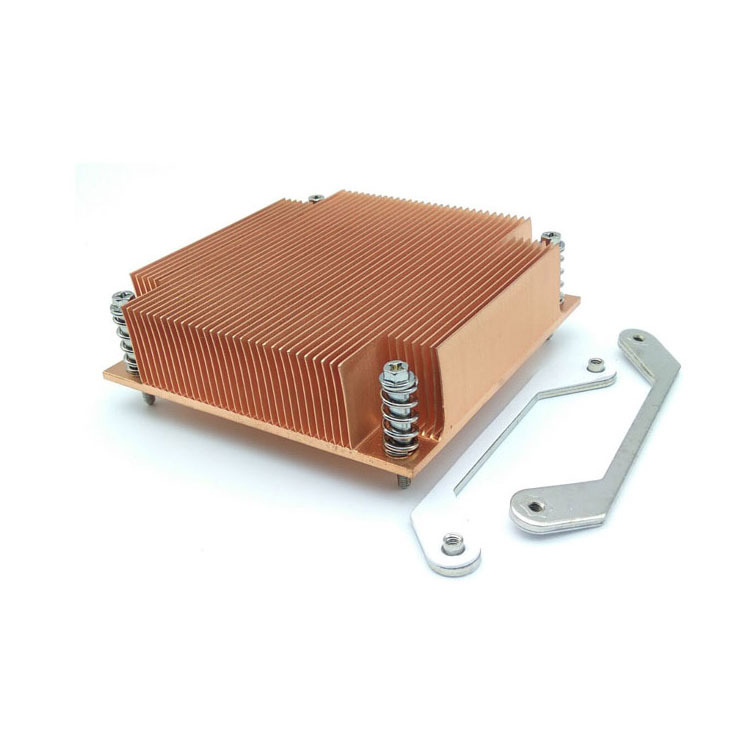
What are Principles of Aluminum Heat Sink Design?
Aluminum heat sink design revolves around optimizing thermal conductivity and maximizing surface area. The design principles include:
• Fin Shape and Size: Fins should be designed to maximize airflow and heat dissipation. Different fin shapes, such as straight, louvered, or pin fins, offer varying levels of performance based on the specific cooling requirements.
• Fin Spacing: Proper spacing ensures efficient airflow between fins, enhancing cooling performance. The spacing should be optimized to balance the resistance to airflow and the heat dissipation capabilities.
• Orientation: Aligning fins with the direction of airflow improves heat transfer. Proper orientation can significantly enhance the cooling efficiency by reducing airflow resistance and improving convective heat transfer.
Other important factors in heat sink design include the base thickness, which should be sufficient to spread the heat evenly across the fins, and the overall dimensions, which should fit within the available space in the electronic assembly.
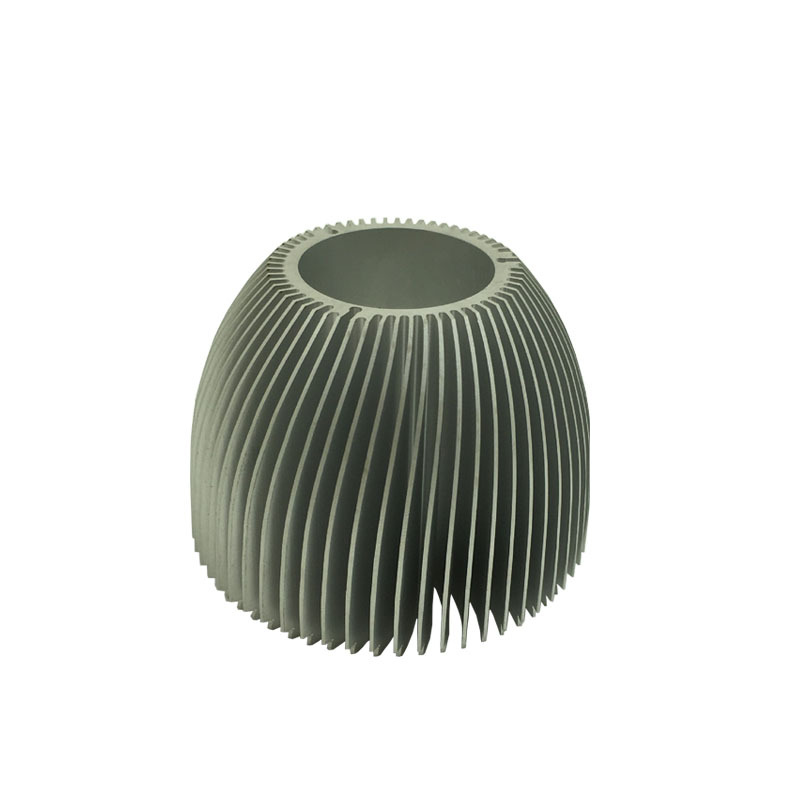

Material Selection for Aluminum Heat Sinks Design
Aluminum is preferred for heat sinks due to its high thermal conductivity, low density, and affordability. Commonly used aluminum alloys include:
• 6061: Known for its strength and good thermal performance. This alloy is easy to machine and offers a good balance of mechanical properties and thermal conductivity.
• 6063: Offers excellent thermal conductivity and is easier to extrude into complex shapes. This alloy is commonly used in applications where intricate heat sink designs are required.
Other aluminum alloys, such as 1050 and 3003, are also used in heat sink manufacturing. The choice of alloy depends on the specific requirements of the application, including thermal performance, mechanical strength, and cost.
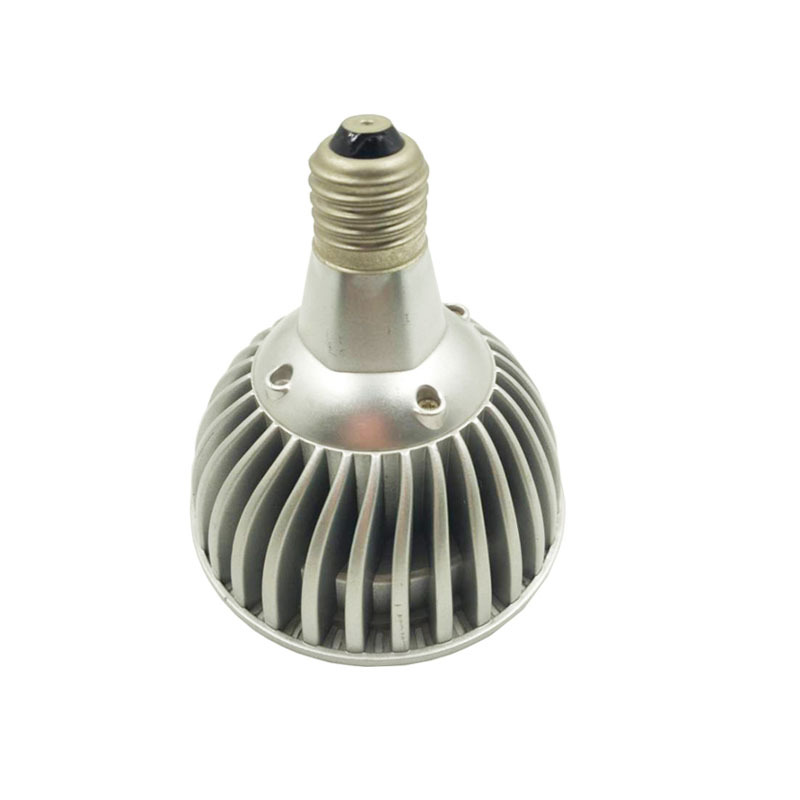

Design Tips for Aluminum Heat Sinks
Effective heat sink design involves considering factors such as thermal resistance, size and shape, and airflow nature. Here are some tips:
• Use Thermal Interface Materials: Improve contact between the heat sink and the device to enhance heat transfer. Thermal pastes, pads, and adhesives can fill microscopic air gaps, reducing thermal resistance and improving heat dissipation.
• Optimize Fin Design: Design fins to maximize convection and minimize airflow resistance. The fin shape, size, and spacing should be tailored to the specific cooling requirements and available airflow.
• Ensure Proper Mounting: Secure the heat sink properly to the device to maintain effective thermal contact. Proper mounting techniques, such as using screws, clips, or adhesives, can ensure stable and efficient heat transfer.
Other design considerations include the use of heat pipes to enhance heat transfer, the incorporation of cooling fans to increase airflow, and the use of surface treatments, such as anodizing, to improve thermal performance and corrosion resistance.

Summary:
In conclusion, aluminum heat sinks play a crucial role in the thermal management of electronic and mechanical devices.
The performance and longevity of their systems can be enhanced by understanding their design principles, applications, and the importance of material selection.
Aluminum heat sinks are versatile and cost-effective solutions for managing heat in a wide range of applications, from computers and power electronics to LED lighting and automotive systems. We hope the information contained in the article will provide you with a deeper understanding of aluminum heat sink.









